点击关注公众号,Java干货及时送达
 学习 Spring Cloud 微服务的正确姿势!
学习 Spring Cloud 微服务的正确姿势!
 用上 ChatGPT 啦,强的离谱!
用上 ChatGPT 啦,强的离谱!
 终于把 Spring Boot 3.0 写成书了!
终于把 Spring Boot 3.0 写成书了!
1.引言
高并发场景在现场的日常工作中很常见,特别是在互联网公司中,这篇文章就来通过秒杀商品来模拟高并发的场景。文章末尾会附上文章的所有代码、脚本和测试用例。
本文环境: SpringBoot 2.5.7 + MySQL 8.0 X + MybatisPlus + Swagger2.9.2
模拟工具: Jmeter
模拟场景: 减库存->创建订单->模拟支付
2.商品秒杀-超卖
在开发中,对于下面的代码,可能很熟悉:在Service里面加上@Transactional事务注解和Lock锁。
Spring Boot 基础就不介绍了,推荐看这个免费教程:
控制层:Controller
@ApiOperation(value="秒杀实现方式——Lock加锁")
@PostMapping("/start/lock")
public Result startLock(long skgId){try {log.info("开始秒杀方式一...");final long userId = (int) (new Random().nextDouble() * (99999 - 10000 + 1)) + 10000;Result result = secondKillService.startSecondKillByLock(skgId, userId);if(result != null){log.info("用户:{}--{}", userId, result.get("msg"));}else{log.info("用户:{}--{}", userId, "哎呦喂,人也太多了,请稍后!");}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {}return Result.ok();
}业务层:Service
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public Result startSecondKillByLock(long skgId, long userId) {lock.lock();try {// 校验库存SecondKill secondKill = secondKillMapper.selectById(skgId);Integer number = secondKill.getNumber();if (number > 0) {// 扣库存secondKill.setNumber(number - 1);secondKillMapper.updateById(secondKill);// 创建订单SuccessKilled killed = new SuccessKilled();killed.setSeckillId(skgId);killed.setUserId(userId);killed.setState((short) 0);killed.setCreateTime(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));successKilledMapper.insert(killed);// 模拟支付Payment payment = new Payment();payment.setSeckillId(skgId);payment.setSeckillId(skgId);payment.setUserId(userId);payment.setMoney(40);payment.setState((short) 1);payment.setCreateTime(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));paymentMapper.insert(payment);} else {return Result.error(SecondKillStateEnum.END);}} catch (Exception e) {throw new ScorpiosException("异常了个乖乖");} finally {lock.unlock();}return Result.ok(SecondKillStateEnum.SUCCESS);
}对于上面的代码应该没啥问题吧,业务方法上加事务,在处理业务的时候加锁。
但上面这样写法是有问题的,会出现超卖的情况,看下测试结果:模拟1000个并发,抢100商品。

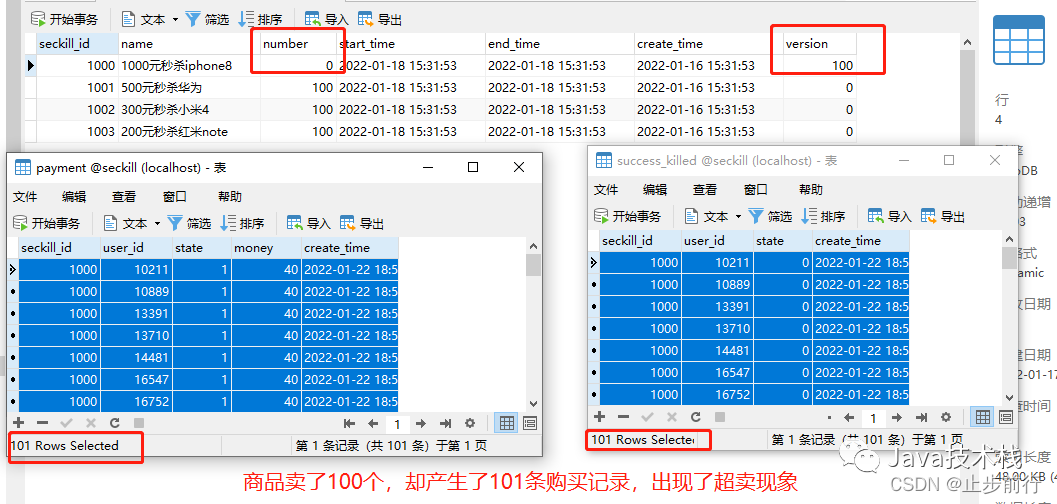
这里在业务方法开始加了锁,在业务方法结束后释放了锁。但这里的事务提交却不是这样的,有可能在事务提交之前,就已经把锁释放了,这样会导致商品超卖现象。所以加锁的时机很重要!
另外,如果你近期准备面试跳槽,建议在Java面试库小程序在线刷题,涵盖 2000+ 道 Java 面试题,几乎覆盖了所有主流技术面试题。
3. 解决商品超卖
对于上面超卖现象,主要问题出现在事务中锁释放的时机,事务未提交之前,锁已经释放。(事务提交是在整个方法执行完)。如何解决这个问题呢,就是把加锁步骤提前
可以在controller层进行加锁
可以使用Aop在业务方法执行之前进行加锁
3.1 方式一(改进版加锁)
@ApiOperation(value="秒杀实现方式——Lock加锁")
@PostMapping("/start/lock")
public Result startLock(long skgId){// 在此处加锁lock.lock();try {log.info("开始秒杀方式一...");final long userId = (int) (new Random().nextDouble() * (99999 - 10000 + 1)) + 10000;Result result = secondKillService.startSecondKillByLock(skgId, userId);if(result != null){log.info("用户:{}--{}", userId, result.get("msg"));}else{log.info("用户:{}--{}", userId, "哎呦喂,人也太多了,请稍后!");}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {// 在此处释放锁lock.unlock();}return Result.ok();
}上面这样的加锁就可以解决事务未提交之前,锁释放的问题,可以分三种情况进行压力测试:
并发数1000,商品100
并发数1000,商品1000
并发数2000,商品1000
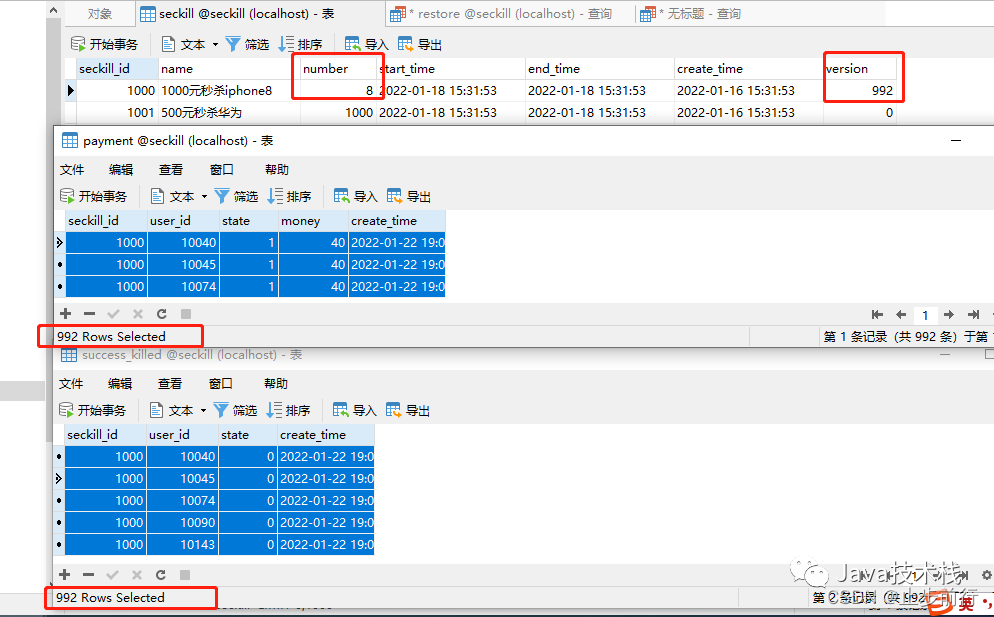
对于并发量大于商品数的情况,商品秒杀一般不会出现少卖的请况,但对于并发数小于等于商品数的时候可能会出现商品少卖情况,这也很好理解。
对于没有问题的情况就不贴图了,因为有很多种方式,贴图会太多
3.2 方式二(AOP版加锁)
对于上面在控制层进行加锁的方式,可能显得不优雅,那就还有另一种方式进行在事务之前加锁,那就是AOP
自定义AOP注解
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ServiceLock {String description() default "";
}定义切面类
@Slf4j
@Component
@Scope
@Aspect
@Order(1) //order越小越是最先执行,但更重要的是最先执行的最后结束
public class LockAspect {/*** 思考:为什么不用synchronized* service 默认是单例的,并发下lock只有一个实例*/private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); // 互斥锁 参数默认false,不公平锁// Service层切点 用于记录错误日志@Pointcut("@annotation(com.scorpios.secondkill.aop.ServiceLock)")public void lockAspect() {}@Around("lockAspect()")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {lock.lock();Object obj = null;try {obj = joinPoint.proceed();} catch (Throwable e) {e.printStackTrace();throw new RuntimeException();} finally{lock.unlock();}return obj;}
}在业务方法上添加AOP注解
@Override
@ServiceLock // 使用Aop进行加锁
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public Result startSecondKillByAop(long skgId, long userId) {try {// 校验库存SecondKill secondKill = secondKillMapper.selectById(skgId);Integer number = secondKill.getNumber();if (number > 0) {//扣库存secondKill.setNumber(number - 1);secondKillMapper.updateById(secondKill);//创建订单SuccessKilled killed = new SuccessKilled();killed.setSeckillId(skgId);killed.setUserId(userId);killed.setState((short) 0);killed.setCreateTime(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));successKilledMapper.insert(killed);//支付Payment payment = new Payment();payment.setSeckillId(skgId);payment.setSeckillId(skgId);payment.setUserId(userId);payment.setMoney(40);payment.setState((short) 1);payment.setCreateTime(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));paymentMapper.insert(payment);} else {return Result.error(SecondKillStateEnum.END);}} catch (Exception e) {throw new ScorpiosException("异常了个乖乖");}return Result.ok(SecondKillStateEnum.SUCCESS);
}控制层:
@ApiOperation(value="秒杀实现方式二——Aop加锁")
@PostMapping("/start/aop")
public Result startAop(long skgId){try {log.info("开始秒杀方式二...");final long userId = (int) (new Random().nextDouble() * (99999 - 10000 + 1)) + 10000;Result result = secondKillService.startSecondKillByAop(skgId, userId);if(result != null){log.info("用户:{}--{}", userId, result.get("msg"));}else{log.info("用户:{}--{}", userId, "哎呦喂,人也太多了,请稍后!");}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}return Result.ok();
}这种方式在对锁的使用上,更高阶、更美观!
3.3 方式三(悲观锁一)
除了上面在业务代码层面加锁外,还可以使用数据库自带的锁进行并发控制。
悲观锁,什么是悲观锁呢?通俗的说,在做任何事情之前,都要进行加锁确认。这种数据库级加锁操作效率较低。
使用for update一定要加上事务,当事务处理完后,for update才会将行级锁解除
如果请求数和秒杀商品数量一致,会出现少卖
@ApiOperation(value="秒杀实现方式三——悲观锁")
@PostMapping("/start/pes/lock/one")
public Result startPesLockOne(long skgId){try {log.info("开始秒杀方式三...");final long userId = (int) (new Random().nextDouble() * (99999 - 10000 + 1)) + 10000;Result result = secondKillService.startSecondKillByUpdate(skgId, userId);if(result != null){log.info("用户:{}--{}", userId, result.get("msg"));}else{log.info("用户:{}--{}", userId, "哎呦喂,人也太多了,请稍后!");}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}return Result.ok();
}业务逻辑
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public Result startSecondKillByUpdate(long skgId, long userId) {try {// 校验库存-悲观锁SecondKill secondKill = secondKillMapper.querySecondKillForUpdate(skgId);Integer number = secondKill.getNumber();if (number > 0) {//扣库存secondKill.setNumber(number - 1);secondKillMapper.updateById(secondKill);//创建订单SuccessKilled killed = new SuccessKilled();killed.setSeckillId(skgId);killed.setUserId(userId);killed.setState((short) 0);killed.setCreateTime(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));successKilledMapper.insert(killed);//支付Payment payment = new Payment();payment.setSeckillId(skgId);payment.setSeckillId(skgId);payment.setUserId(userId);payment.setMoney(40);payment.setState((short) 1);payment.setCreateTime(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));paymentMapper.insert(payment);} else {return Result.error(SecondKillStateEnum.END);}} catch (Exception e) {throw new ScorpiosException("异常了个乖乖");} finally {}return Result.ok(SecondKillStateEnum.SUCCESS);
}Dao层
@Repository
public interface SecondKillMapper extends BaseMapper<SecondKill> {/*** 将此行数据进行加锁,当整个方法将事务提交后,才会解锁* @param skgId* @return*/@Select(value = "SELECT * FROM seckill WHERE seckill_id=#{skgId} FOR UPDATE")SecondKill querySecondKillForUpdate(@Param("skgId") Long skgId);}上面是利用for update进行对查询数据加锁,加的是行锁。
点击关注公众号,Java干货及时送达
3.4 方式四(悲观锁二)
悲观锁的第二种方式就是利用update更新命令来加表锁
/*** UPDATE锁表* @param skgId 商品id* @param userId 用户id* @return*/
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public Result startSecondKillByUpdateTwo(long skgId, long userId) {try {// 不校验,直接扣库存更新int result = secondKillMapper.updateSecondKillById(skgId);if (result > 0) {//创建订单SuccessKilled killed = new SuccessKilled();killed.setSeckillId(skgId);killed.setUserId(userId);killed.setState((short) 0);killed.setCreateTime(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));successKilledMapper.insert(killed);//支付Payment payment = new Payment();payment.setSeckillId(skgId);payment.setSeckillId(skgId);payment.setUserId(userId);payment.setMoney(40);payment.setState((short) 1);payment.setCreateTime(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));paymentMapper.insert(payment);} else {return Result.error(SecondKillStateEnum.END);}} catch (Exception e) {throw new ScorpiosException("异常了个乖乖");} finally {}return Result.ok(SecondKillStateEnum.SUCCESS);
}Dao层
@Repository
public interface SecondKillMapper extends BaseMapper<SecondKill> {/*** 将此行数据进行加锁,当整个方法将事务提交后,才会解锁* @param skgId* @return*/@Select(value = "SELECT * FROM seckill WHERE seckill_id=#{skgId} FOR UPDATE")SecondKill querySecondKillForUpdate(@Param("skgId") Long skgId);@Update(value = "UPDATE seckill SET number=number-1 WHERE seckill_id=#{skgId} AND number > 0")int updateSecondKillById(@Param("skgId") long skgId);
}3.5 方式五(乐观锁)
乐观锁,顾名思义,就是对操作结果很乐观,通过利用version字段来判断数据是否被修改
乐观锁,不进行库存数量的校验,直接做库存扣减
这里使用的乐观锁会出现大量的数据更新异常(抛异常就会导致购买失败)、如果配置的抢购人数比较少、比如120:100(人数:商品) 会出现少买的情况,不推荐使用乐观锁。
@ApiOperation(value="秒杀实现方式五——乐观锁")
@PostMapping("/start/opt/lock")
public Result startOptLock(long skgId){try {log.info("开始秒杀方式五...");final long userId = (int) (new Random().nextDouble() * (99999 - 10000 + 1)) + 10000;// 参数添加了购买数量Result result = secondKillService.startSecondKillByPesLock(skgId, userId,1);if(result != null){log.info("用户:{}--{}", userId, result.get("msg"));}else{log.info("用户:{}--{}", userId, "哎呦喂,人也太多了,请稍后!");}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}return Result.ok();
}
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public Result startSecondKillByPesLock(long skgId, long userId, int number) {// 乐观锁,不进行库存数量的校验,直接try {SecondKill kill = secondKillMapper.selectById(skgId);// 剩余的数量应该要大于等于秒杀的数量if(kill.getNumber() >= number) {int result = secondKillMapper.updateSecondKillByVersion(number,skgId,kill.getVersion());if (result > 0) {//创建订单SuccessKilled killed = new SuccessKilled();killed.setSeckillId(skgId);killed.setUserId(userId);killed.setState((short) 0);killed.setCreateTime(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));successKilledMapper.insert(killed);//支付Payment payment = new Payment();payment.setSeckillId(skgId);payment.setSeckillId(skgId);payment.setUserId(userId);payment.setMoney(40);payment.setState((short) 1);payment.setCreateTime(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));paymentMapper.insert(payment);} else {return Result.error(SecondKillStateEnum.END);}}} catch (Exception e) {throw new ScorpiosException("异常了个乖乖");} finally {}return Result.ok(SecondKillStateEnum.SUCCESS);
}
@Repository
public interface SecondKillMapper extends BaseMapper<SecondKill> {/*** 将此行数据进行加锁,当整个方法将事务提交后,才会解锁* @param skgId* @return*/@Select(value = "SELECT * FROM seckill WHERE seckill_id=#{skgId} FOR UPDATE")SecondKill querySecondKillForUpdate(@Param("skgId") Long skgId);@Update(value = "UPDATE seckill SET number=number-1 WHERE seckill_id=#{skgId} AND number > 0")int updateSecondKillById(@Param("skgId") long skgId);@Update(value = "UPDATE seckill SET number=number-#{number},version=version+1 WHERE seckill_id=#{skgId} AND version = #{version}")int updateSecondKillByVersion(@Param("number") int number, @Param("skgId") long skgId, @Param("version")int version);
}乐观锁会出现大量的数据更新异常(抛异常就会导致购买失败),会出现少买的情况,不推荐使用乐观锁。
锁是面试必问的,如果你近期准备面试跳槽,建议在Java面试库小程序在线刷题,涵盖 2000+ 道 Java 面试题,几乎覆盖了所有主流技术面试题。
3.6 方式六(阻塞队列)
利用阻塞队类,也可以解决高并发问题。其思想就是把接收到的请求按顺序存放到队列中,消费者线程逐一从队列里取数据进行处理,看下具体代码。
阻塞队列:这里使用静态内部类的方式来实现单例模式,在并发条件下不会出现问题。
// 秒杀队列(固定长度为100)
public class SecondKillQueue {// 队列大小static final int QUEUE_MAX_SIZE = 100;// 用于多线程间下单的队列static BlockingQueue<SuccessKilled> blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<SuccessKilled>(QUEUE_MAX_SIZE);// 使用静态内部类,实现单例模式private SecondKillQueue(){};private static class SingletonHolder{// 静态初始化器,由JVM来保证线程安全private static SecondKillQueue queue = new SecondKillQueue();}/*** 单例队列* @return*/public static SecondKillQueue getSkillQueue(){return SingletonHolder.queue;}/*** 生产入队* @param kill* @throws InterruptedException* add(e) 队列未满时,返回true;队列满则抛出IllegalStateException(“Queue full”)异常——AbstractQueue* put(e) 队列未满时,直接插入没有返回值;队列满时会阻塞等待,一直等到队列未满时再插入。* offer(e) 队列未满时,返回true;队列满时返回false。非阻塞立即返回。* offer(e, time, unit) 设定等待的时间,如果在指定时间内还不能往队列中插入数据则返回false,插入成功返回true。*/public Boolean produce(SuccessKilled kill) {return blockingQueue.offer(kill);}/*** 消费出队* poll() 获取并移除队首元素,在指定的时间内去轮询队列看有没有首元素有则返回,否者超时后返回null* take() 与带超时时间的poll类似不同在于take时候如果当前队列空了它会一直等待其他线程调用notEmpty.signal()才会被唤醒*/public SuccessKilled consume() throws InterruptedException {return blockingQueue.take();}/*** 获取队列大小* @return*/public int size() {return blockingQueue.size();}
}消费秒杀队列:实现ApplicationRunner接口
// 消费秒杀队列
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TaskRunner implements ApplicationRunner{@Autowiredprivate SecondKillService seckillService;@Overridepublic void run(ApplicationArguments var){new Thread(() -> {log.info("队列启动成功");while(true){try {// 进程内队列SuccessKilled kill = SecondKillQueue.getSkillQueue().consume();if(kill != null){Result result = seckillService.startSecondKillByAop(kill.getSeckillId(), kill.getUserId());if(result != null && result.equals(Result.ok(SecondKillStateEnum.SUCCESS))){log.info("TaskRunner,result:{}",result);log.info("TaskRunner从消息队列取出用户,用户:{}{}",kill.getUserId(),"秒杀成功");}}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}).start();}
}
@ApiOperation(value="秒杀实现方式六——消息队列")
@PostMapping("/start/queue")
public Result startQueue(long skgId){try {log.info("开始秒杀方式六...");final long userId = (int) (new Random().nextDouble() * (99999 - 10000 + 1)) + 10000;SuccessKilled kill = new SuccessKilled();kill.setSeckillId(skgId);kill.setUserId(userId);Boolean flag = SecondKillQueue.getSkillQueue().produce(kill);// 虽然进入了队列,但是不一定能秒杀成功 进队出队有时间间隙if(flag){log.info("用户:{}{}",kill.getUserId(),"秒杀成功");}else{log.info("用户:{}{}",userId,"秒杀失败");}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}return Result.ok();
}使用阻塞队列来实现秒杀,有几点要注意:
消费秒杀队列中调用业务方法加锁与不加锁情况一样,也就是
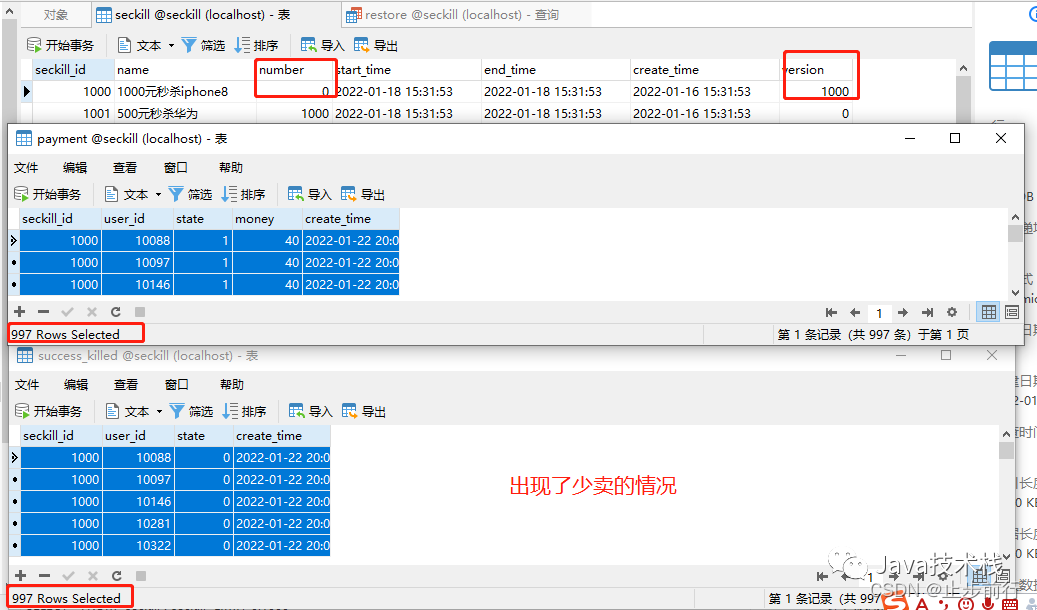
seckillService.startSecondKillByAop()、seckillService.startSecondKillByLock()方法结果一样,这也很好理解当队列长度与商品数量一致时,会出现少卖的现象,可以调大数值
下面是队列长度1000,商品数量1000,并发数2000情况下出现的少卖
3.7.方式七(Disruptor队列)
Disruptor是个高性能队列,研发的初衷是解决内存队列的延迟问题,在性能测试中发现竟然与I/O操作处于同样的数量级,基于Disruptor开发的系统单线程能支撑每秒600万订单。
// 事件生成工厂(用来初始化预分配事件对象)
public class SecondKillEventFactory implements EventFactory<SecondKillEvent> {@Overridepublic SecondKillEvent newInstance() {return new SecondKillEvent();}
}
// 事件对象(秒杀事件)
public class SecondKillEvent implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;private long seckillId;private long userId;// set/get方法略}
// 使用translator方式生产者
public class SecondKillEventProducer {private final static EventTranslatorVararg<SecondKillEvent> translator = (seckillEvent, seq, objs) -> {seckillEvent.setSeckillId((Long) objs[0]);seckillEvent.setUserId((Long) objs[1]);};private final RingBuffer<SecondKillEvent> ringBuffer;public SecondKillEventProducer(RingBuffer<SecondKillEvent> ringBuffer){this.ringBuffer = ringBuffer;}public void secondKill(long seckillId, long userId){this.ringBuffer.publishEvent(translator, seckillId, userId);}
}
// 消费者(秒杀处理器)
@Slf4j
public class SecondKillEventConsumer implements EventHandler<SecondKillEvent> {private SecondKillService secondKillService = (SecondKillService) SpringUtil.getBean("secondKillService");@Overridepublic void onEvent(SecondKillEvent seckillEvent, long seq, boolean bool) {Result result = secondKillService.startSecondKillByAop(seckillEvent.getSeckillId(), seckillEvent.getUserId());if(result.equals(Result.ok(SecondKillStateEnum.SUCCESS))){log.info("用户:{}{}",seckillEvent.getUserId(),"秒杀成功");}}
}
public class DisruptorUtil {static Disruptor<SecondKillEvent> disruptor;static{SecondKillEventFactory factory = new SecondKillEventFactory();int ringBufferSize = 1024;ThreadFactory threadFactory = runnable -> new Thread(runnable);disruptor = new Disruptor<>(factory, ringBufferSize, threadFactory);disruptor.handleEventsWith(new SecondKillEventConsumer());disruptor.start();}public static void producer(SecondKillEvent kill){RingBuffer<SecondKillEvent> ringBuffer = disruptor.getRingBuffer();SecondKillEventProducer producer = new SecondKillEventProducer(ringBuffer);producer.secondKill(kill.getSeckillId(),kill.getUserId());}
}
@ApiOperation(value="秒杀实现方式七——Disruptor队列")
@PostMapping("/start/disruptor")
public Result startDisruptor(long skgId){try {log.info("开始秒杀方式七...");final long userId = (int) (new Random().nextDouble() * (99999 - 10000 + 1)) + 10000;SecondKillEvent kill = new SecondKillEvent();kill.setSeckillId(skgId);kill.setUserId(userId);DisruptorUtil.producer(kill);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}return Result.ok();
}经过测试,发现使用Disruptor队列队列,与自定义队列有着同样的问题,也会出现超卖的情况,但效率有所提高。
4. 小结
对于上面七种实现并发的方式,做一下总结:
一、二方式是在代码中利用锁和事务的方式解决了并发问题,主要解决的是锁要加载事务之前
三、四、五方式主要是数据库的锁来解决并发问题,方式三是利用for upate对表加行锁,方式四是利用update来对表加锁,方式五是通过增加version字段来控制数据库的更新操作,方式五的效果最差
六、七方式是通过队列来解决并发问题,这里需要特别注意的是,在代码中不能通过throw抛异常,否则消费线程会终止,而且由于进队和出队存在时间间隙,会导致商品少卖
上面所有的情况都经过代码测试,测试分一下三种情况:
并发数1000,商品数100
并发数1000,商品数1000
并发数2000,商品数1000
思考:分布式情况下如何解决并发问题呢?下次继续试验。
最后宣传下我的 ChatGPT 知识星球,R哥最近 ChatGPT 玩疯了,用它写文章、生成代码、做表格、写 PPT、写文案、做面试题,效率提升了 N 倍。
建议尽快上车,现在上手成本是越来越高了,不割韭菜,R哥是实实在在教大家东西。
星球分享了大量 ChatGPT 学习资料, 还输出了 50+ 篇保姆级教程,持续更新中,涉及方方面面,真正的高质量知识星球。
目前还是优惠价,快扫码加入吧:

1000 人后正式涨价啦,早就是优势!
End
 学习 Spring Cloud 微服务的正确姿势!
学习 Spring Cloud 微服务的正确姿势!
 博客园在绝境求生。。
博客园在绝境求生。。
 用上 ChatGPT 啦,强的离谱!
用上 ChatGPT 啦,强的离谱!
 吴恩达 ChatGPT 免费视频课程来了!
吴恩达 ChatGPT 免费视频课程来了!
 Java 20 正式发布,超神了。。
Java 20 正式发布,超神了。。
👇 点击阅读原文,玩转 ChatGPT!
本文链接:https://my.lmcjl.com/post/13191.html

4 评论