爬取目标站点分析
本次采集的目标站点为:https://www.zaih.com/falcon/mentors,目标数据为在行高手数据。
本次数据保存到 MySQL 数据库中,基于目标数据,设计表结构如下所示。
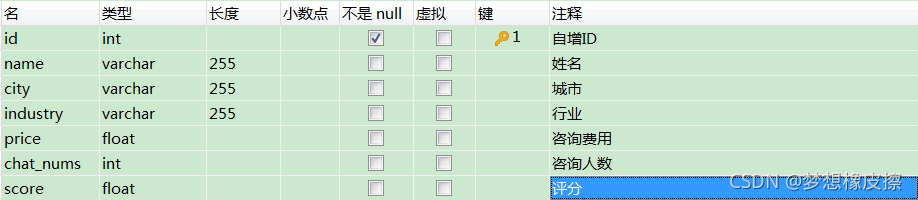
对比表结构,可以直接将 scrapy 中的 items.py 文件编写完毕。
class ZaihangItem(scrapy.Item): # define the fields for your item here like: name = scrapy.Field() # 姓名 city = scrapy.Field() # 城市 industry = scrapy.Field() # 行业 price = scrapy.Field() # 价格 chat_nums = scrapy.Field() # 聊天人数 score = scrapy.Field() # 评分
编码时间
项目的创建过程参考上一案例即可,本文直接从采集文件开发进行编写,该文件为 zh.py。
本次目标数据分页地址需要手动拼接,所以提前声明一个实例变量(字段),该字段为 page,每次响应之后,判断数据是否为空,如果不为空,则执行 +1 操作。
请求地址模板如下:
https://www.zaih.com/falcon/mentors?first_tag_id=479&first_tag_name=心理&page={}
当页码超过最大页数时,返回如下页面状态,所以数据为空状态,只需要判断 是否存在 class=empty 的 section 即可。
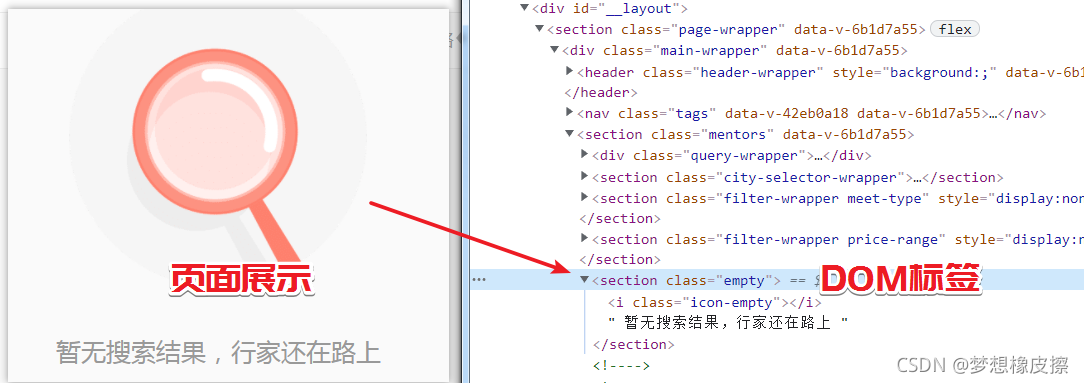
解析数据与数据清晰直接参考下述代码即可。
import scrapy
from zaihang_spider.items import ZaihangItem
class ZhSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'zh'
allowed_domains = ['www.zaih.com']
page = 1 # 起始页码
url_format = 'https://www.zaih.com/falcon/mentors?first_tag_id=479&first_tag_name=%E5%BF%83%E7%90%86&page={}' # 模板
start_urls = [url_format.format(page)]
def parse(self, response):
empty = response.css("section.empty") # 判断数据是否为空
if len(empty) > 0:
return # 存在空标签,直接返回
mentors = response.css(".mentor-board a") # 所有高手的超链接
for m in mentors:
item = ZaihangItem() # 实例化一个对象
name = m.css(".mentor-card__name::text").extract_first()
city = m.css(".mentor-card__location::text").extract_first()
industry = m.css(".mentor-card__title::text").extract_first()
price = self.replace_space(m.css(".mentor-card__price::text").extract_first())
chat_nums = self.replace_space(m.css(".mentor-card__number::text").extract()[0])
score = self.replace_space(m.css(".mentor-card__number::text").extract()[1])
# 格式化数据
item["name"] = name
item["city"] = city
item["industry"] = industry
item["price"] = price
item["chat_nums"] = chat_nums
item["score"] = score
yield item
# 再次生成一个请求
self.page += 1
next_url = format(self.url_format.format(self.page))
yield scrapy.Request(url=next_url, callback=self.parse)
def replace_space(self, in_str):
in_str = in_str.replace("\n", "").replace("\r", "").replace("¥", "")
return in_str.strip()
开启 settings.py 文件中的 ITEM_PIPELINES,注意类名有修改
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'zaihang_spider.pipelines.ZaihangMySQLPipeline': 300,
}
修改 pipelines.py 文件,使其能将数据保存到 MySQL 数据库中
在下述代码中,首先需要了解类方法 from_crawler,该方法是 __init__ 的一个代理,如果其存在,类被初始化时会被调用,并得到全局的 crawler,然后通过 crawler 就可以获取 settings.py 中的各个配置项。
除此之外,还存在一个 from_settings 方法,一般在官方插件中也有应用,示例如下所示。
@classmethod
def from_settings(cls, settings):
host= settings.get('HOST')
return cls(host)
@classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
# FIXME: for now, stats are only supported from this constructor
return cls.from_settings(crawler.settings)
在编写下述代码前,需要提前在 settings.py 中写好配置项。
settings.py 文件代码
HOST = "127.0.0.1" PORT = 3306 USER = "root" PASSWORD = "123456" DB = "zaihang"
pipelines.py 文件代码
import pymysql
class ZaihangMySQLPipeline:
def __init__(self, host, port, user, password, db):
self.host = host
self.port = port
self.user = user
self.password = password
self.db = db
self.conn = None
self.cursor = None
@classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
return cls(
host=crawler.settings.get('HOST'),
port=crawler.settings.get('PORT'),
user=crawler.settings.get('USER'),
password=crawler.settings.get('PASSWORD'),
db=crawler.settings.get('DB')
)
def open_spider(self, spider):
self.conn = pymysql.connect(host=self.host, port=self.port, user=self.user, password=self.password, db=self.db)
def process_item(self, item, spider):
# print(item)
# 存储到 MySQL
name = item["name"]
city = item["city"]
industry = item["industry"]
price = item["price"]
chat_nums = item["chat_nums"]
score = item["score"]
sql = "insert into users(name,city,industry,price,chat_nums,score) values ('%s','%s','%s',%.1f,%d,%.1f)" % (
name, city, industry, float(price), int(chat_nums), float(score))
print(sql)
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor() # 设置游标
try:
self.cursor.execute(sql) # 执行 sql
self.conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
print(e)
self.conn.rollback()
return item
def close_spider(self, spider):
self.cursor.close()
self.conn.close()
管道文件中三个重要函数,分别是 open_spider,process_item,close_spider。
# 爬虫开启时执行,只执行一次 def open_spider(self, spider): # spider.name = "橡皮擦" # spider对象动态添加实例变量,可以在spider模块中获取该变量值,比如在 parse(self, response) 函数中通过self 获取属性 # 一些初始化动作 pass # 处理提取的数据,数据保存代码编写位置 def process_item(self, item, spider): pass # 爬虫关闭时执行,只执行一次,如果爬虫运行过程中发生异常崩溃,close_spider 不会执行 def close_spider(self, spider): # 关闭数据库,释放资源 pass
爬取结果展示

以以上就是python实战项目scrapy管道学习爬取在行高手数据的详细内容,更多关于python scrapy管道学习爬取在行的资料请关注服务器之家其它相关文章!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/hihell/article/details/120934425
本文链接:https://my.lmcjl.com/post/3699.html

4 评论