一、是什么
1、概念
2、优点
3、缺点
二、架构模式
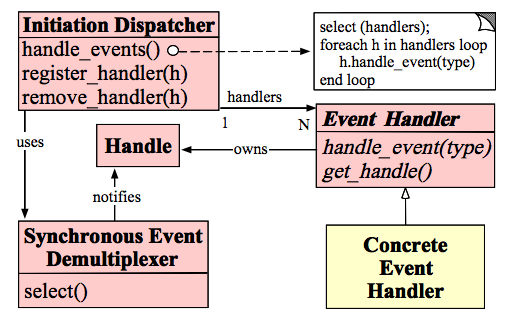
1、架构图
2、构成
Handles :表示操作系统管理的资源,我们可以理解为fd。
Synchronous Event Demultiplexer :同步事件分离器,阻塞等待Handles中的事件发生。
Initiation Dispatcher :初始分派器,作用为添加Event handler(事件处理器)、删除Event handler以及分派事件给Event handler。也就是说,Synchronous Event Demultiplexer负责等待新事件发生,事件发生时通知Initiation Dispatcher,然后Initiation Dispatcher调用event handler处理事件。
Event Handler :事件处理器的接口
Concrete Event Handler :事件处理器的实际实现,而且绑定了一个Handle。因为在实际情况中,我们往往不止一种事件处理器,因此这里将事件处理器接口和实现分开,与C++、Java这些高级语言中的多态类似。
3、模块交互
三、代码注释
package com.linxcool.reactor; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set; /** * 反应器模式 * 用于解决多用户访问并发问题 * * 举个例子:餐厅服务问题 * * 传统线程池做法:来一个客人(请求)去一个服务员(线程) * 反应器模式做法:当客人点菜的时候,服务员就可以去招呼其他客人了,等客人点好了菜,直接招呼一声“服务员” * * @author linxcool */
public class Reactor implements Runnable{ public final Selector selector; public final ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel; public Reactor(int port) throws IOException{ selector=Selector.open(); serverSocketChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open(); InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress=new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getLocalHost(),port); serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(inetSocketAddress); serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); //向selector注册该channel SelectionKey selectionKey=serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); //利用selectionKey的attache功能绑定Acceptor 如果有事情,触发Acceptor selectionKey.attach(new Acceptor(this)); } @Override public void run() { try { while(!Thread.interrupted()){ selector.select(); Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys= selector.selectedKeys(); Iterator<SelectionKey> it=selectionKeys.iterator(); //Selector如果发现channel有OP_ACCEPT或READ事件发生,下列遍历就会进行。 while(it.hasNext()){ //来一个事件 第一次触发一个accepter线程 //以后触发SocketReadHandler SelectionKey selectionKey=it.next(); dispatch(selectionKey); selectionKeys.clear(); } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 运行Acceptor或SocketReadHandler * @param key */ void dispatch(SelectionKey key) { Runnable r = (Runnable)(key.attachment()); if (r != null){ r.run(); } } }
package com.linxcool.reactor; import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; public class Acceptor implements Runnable{ private Reactor reactor; public Acceptor(Reactor reactor){ this.reactor=reactor; } @Override public void run() { try { SocketChannel socketChannel=reactor.serverSocketChannel.accept(); if(socketChannel!=null)//调用Handler来处理channel new SocketReadHandler(reactor.selector, socketChannel); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
}
package com.linxcool.reactor; import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; public class SocketReadHandler implements Runnable{ private SocketChannel socketChannel; public SocketReadHandler(Selector selector,SocketChannel socketChannel) throws IOException{ this.socketChannel=socketChannel; socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); SelectionKey selectionKey=socketChannel.register(selector, 0); //将SelectionKey绑定为本Handler 下一步有事件触发时,将调用本类的run方法。 //参看dispatch(SelectionKey key) selectionKey.attach(this); //同时将SelectionKey标记为可读,以便读取。 selectionKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ); selector.wakeup(); } /** * 处理读取数据 */ @Override public void run() { ByteBuffer inputBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); inputBuffer.clear(); try { socketChannel.read(inputBuffer); //激活线程池 处理这些request //requestHandle(new Request(socket,btt)); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
}
总结:
本文链接:https://my.lmcjl.com/post/9410.html
展开阅读全文

4 评论