一、前言
在java中,和C语言一样,也有关于字符串的定义,并且有他自己特有的功能,下面我们一起来学习一下。
二、String类概述
string在软件包java.lang下,所以不需要导包。
String字符串是java中的重点,String 类表示字符串类 ,所有的字符串(如"adf")都属于
此类,也就是说有" "双引号括起来的都属于此类,
三、字符串的特点
字符串不可变,他们的值在创建之后不能被改变。
虽然String的值的不可变的,但是他们可以被共享。共享就是其他成员也可以拥有这个值,
字符串效果相当于数组(char[] ),但是底层原理是字节数组(byte[] )
jdk8以前是字符数组,jdk9以后是字节数组。
四、String 构造方法
public String() //创建一个空白字符串对象,不含有任何内容。 public String(char[] ch)//根据字符数组的内容来创建字符对象。 public String (byte[] b)//根据字节数组的内容来创建字节对象。 String s=“abc” //字节赋值的方式创建对象,内容就是abc。
图示:
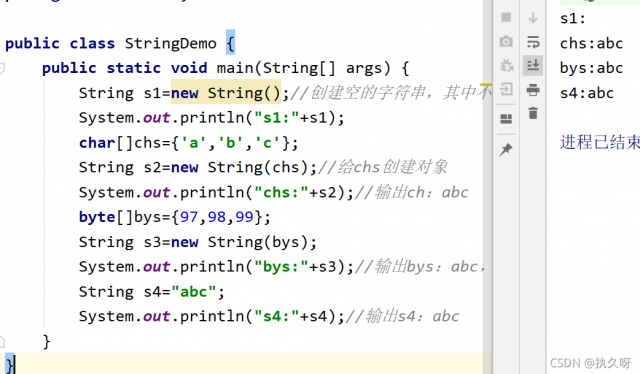
代码演示:
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1=new String();//创建空的字符串,其中不包括任何内容
System.out.println("s1:"+s1);
char[]chs={'a','b','c'};
String s2=new String(chs);//给chs创建对象
System.out.println("chs:"+s2);//输出ch:abc
byte[]bys={97,98,99};
String s3=new String(bys);
System.out.println("bys:"+s3);//输出bys:abc,他会 转化成对应的Ascll码值
String s4="abc";
System.out.println("s4:"+s4);//输出s4:abc
}
}
综上看,推荐使用直接赋值的方式得到字符串对象。
五、String类对象的特点
通过new创建的的字符串对象,每一次new都会申请一个内存空间,虽然内容一样,但是地址不同
六、比较字符串的方法
我们在比较两个数字是否相同时,一般用的是==来判断,那么要比较两个字符串相等
用的是什么呢,答案是用equals。
用法:
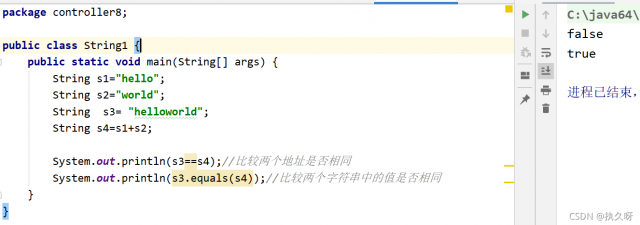
public class String1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1="hello";
String s2="world";
String s3= "helloworld";
String s4=s1+s2;
System.out.println(s7==s8);//0
System.out.println(s3==s4);//比较两个字符串的地址是否相同
System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));//比较两个字符串中的值是否相同
}
}
代码图示:
原因下文分析。
七、判断两个字符串地址是否相等
在字符串中,两个字符串相加可以的到一个新的字符串,这是我们知道的,但是地址会是一样的吗
看下列代码:
public class String1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1="hello";
String s2="world";
String s3= "helloworld";
String s4=s1+s2;
String s5="he"+"llo";
String s6="hello"+"world";
String s7="hello"+s2;
String s8=s1+"world";
System.out.println(s3==s6);//比较两个地址是否相同
System.out.println(s1==s5);
System.out.println(s3==s7);
System.out.println(s3==s8);
System.out.println(s7==s8);
System.out.println(s3==s4);
System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));//比较两个字符串中的值是否相同
}
}
我们仔细分析:
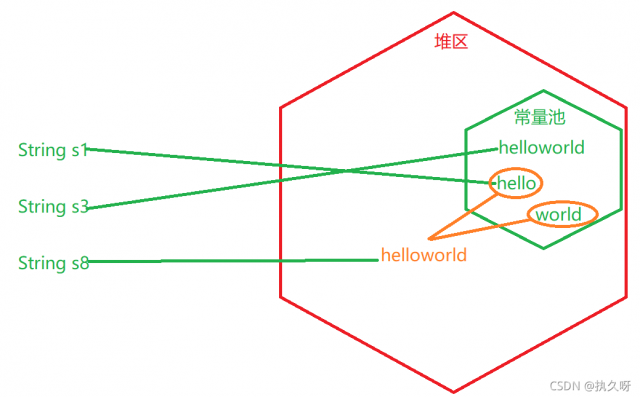
第一个:
String s3= "helloworld"; String s6="hello"+"world";
第二个:
String s1="hello"; String s5="he"+"llo";
第三个:
String s2="world"; String s3= "helloworld"; String s7="hello"+s2;
StringBuilder和StringBuffer的区别
- 1.StringBuffer 对几乎所有的方法都实现了同步,线程比较安全,在多线程系统中可以保
- 证数据同步。
- 2.StringBuilder 没有实现同步,线程不安全,在多线程系统中不能使用 StringBuilder。
- 3.当需要考虑线程安全的场景下使用 StringBuffer,如果不需要考虑线程安全,追求效率的场
- 景下可以使用 StringBuilder。
第四个:
String s1="hello"; String s3= "helloworld"; String s8=s1+"world";
第五个:
String s1="hello";
String s2="world";
String s7="hello"+s2;
String s8=s1+"world";
第六个:
String s1="hello"; String s2="world"; String s3= "helloworld"; String s4=s1+s2;
到此这篇关于关于Java中String类字符串的解析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java中String类字符串内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_60719453/article/details/120746827
本文链接:https://my.lmcjl.com/post/15890.html

4 评论