传统I/O模式
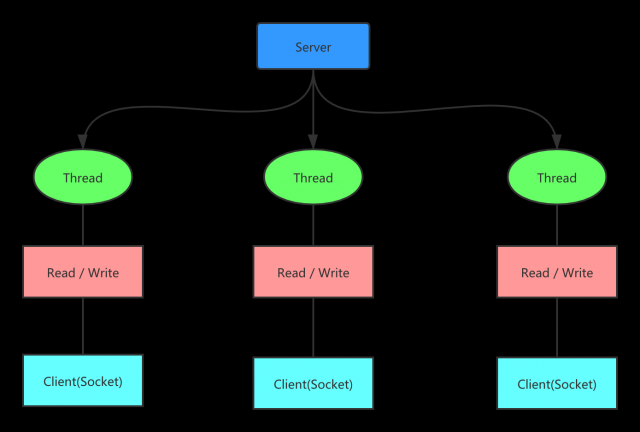
- 我们之前的的I/O文章中有过如下这种图:
-
如上模型中,存在的问题
- 当并发数量很大的时候,会创建大量的线程,占用很大的系统资源
- 当连接创建后,如果当前线程暂时没有可以读的数据,那么改县城会阻塞在read的操作上,造成资源的浪费
-
基于以上的问题,大师Doug Lea出了一篇关于分析与构建可伸缩的高性能IO服务的经典文章《Scalable IO in Java》;在文章中Doug Lea通过各个角度,循序渐进的梳理了服务开发中的相关问题,以及在解决问题的过程中服务模型的演变与进化,文章中基于Reactor反应器模式的几种服务模型架构,也被Netty、Mina等大多数高性能IO服务框架所采用,因此阅读这篇文章有助于你更深入了解Netty、Mina等服务框架的编程思想与设计模式。同时Doug Lea 也是java.util.concurrent包的作者,大师当之无愧
Reactor 模式
针对传统I/O的服务模式优化
- 基于I/O复用模型:多个连接公用一个阻塞的对象,应用程序只需要在一个阻塞对象等待,无需阻塞等待所有的连接,当某个连接有新的数据需要处理的时候,操作系统在通知应用陈旭,唤醒线程,线程从阻塞态返回,开始处理业务:
- 基于线程池复用技术实现一个线程池:不用每次来一个连接创建一个线程,我们将连接完成后的业务处理任务分配给线程池处理,一个线程池可以处理多个连接的业务。
- 如上两点优化如下:
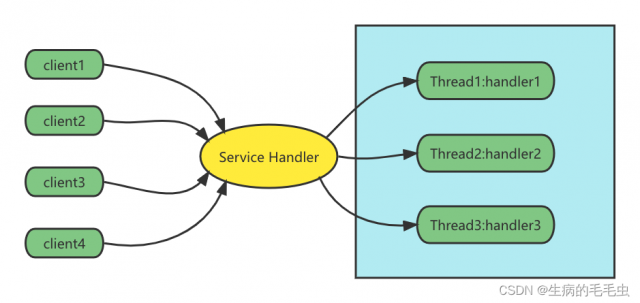
Reactor模式基本设计思路
- 上图中其实基本描述了Reactor的基本思想,我们用如下图细化

- 入上图:
- Reactor模式,通过一个活着多个输入同时传递给服务处理器的模式(基于事件的模式)
- 服务器端程序处理传入的多个请求,并且将它们同步分派到对应的处理线程,因此,Reactor模式也可以叫Dispatcher模式
- Readtor模式使用I/O复用监听事件,收到事件通知后,分发给某个线程(进程),这种设计就是网络服务高并发处理的关键。
Reactor模式中核心组成
- Reactor:Reactor模式在一个单独的线程中运行,负责监听和分发事件,分发给适当的处理程序来处理对应的I/O事件。就类似Nginx的转发,他负责接收来自客户端的请求并且将请求转发到对应的不同服务来处理
- Handlers:处理程序执行I/O事件要完成的实际事件,类似于Nginx转发之后给对应的接口的具体实现。Reactor通过一定的规则来找到对应的处理逻辑来响应I/O事件,处理程序执行非阻塞操作。
Reactor模式分类
- 根据Reactor的数量和处理资源线程池的数量不同,有3种实现模式
- 单Reactor单线程模式
- 单Reactor多线程模式
- 主从Reactor多线程模式
单Reactor单线程模式
- 原理图如下下:

-
用如下NIO简单群聊系统来验证单Reactor单线程模式
-
Client 端代码
/*** 群聊客户端* @author liaojiamin* @Date:Created in 16:03 2022/8/22*/
public class GroupChatClient {private SocketChannel socketChannel;private Selector selector;private Integer port = 6667;private String HOST = "127.0.0.1";private String userName;/*** 初始化* */public GroupChatClient() throws IOException {socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress(HOST, port));selector = Selector.open();socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);userName = socketChannel.getLocalAddress().toString().substring(1);System.out.println(userName + " is ok");}public void sendInfo(String info){info = userName + " say "+ info;try {socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(info.getBytes()));} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public void readInfo(){try{int readChannels = selector.select();if(readChannels > 0){Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();if(selectionKey.isReadable()){SocketChannel readSocketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);readSocketChannel.read(byteBuffer);String msg = new String(byteBuffer.array());System.out.println("读取消息: "+ msg.trim());}iterator.remove();}}else {
// System.out.println("没有可用通道.....");}}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {GroupChatClient groupChatClient = new GroupChatClient();new Thread(){@Overridepublic void run(){while (true){groupChatClient.readInfo();try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(3000);}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}.start();Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);while (scanner.hasNextLine()){String s = scanner.next();groupChatClient.sendInfo(s);}}
}
- Service 端代码
/*** 群聊服务器* @author liaojiamin* @Date:Created in 15:49 2022/8/22*/
public class GroupChatService {private Selector selector;private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;private Integer port = 6667;/*** 数据初始化*/public GroupChatService() {try {selector = Selector.open();serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", port));serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public void listen() {System.out.println("listen thread name "+ Thread.currentThread().getName());try {while (true) {int count = selector.select(2000);if (count > 0) {Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);System.out.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress() + " 上线 ");}if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {readData(selectionKey);}iterator.remove();}}else {
// System.out.println("等待....");}}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {System.out.println("关闭各种管道");}}/*** 读取数据*/public void readData(SelectionKey key) {SocketChannel socketChannel = null;try {socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);int count = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);if (count > 0) {String msg = new String(byteBuffer.array());System.out.println("from 客户端: " + msg);sendInfoToOtherClients(msg, socketChannel);}} catch (IOException e) {try {System.out.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress()+ "离线了....");key.cancel();socketChannel.close();}catch (Exception e1){e1.printStackTrace();}e.printStackTrace();}}/*** 消息转发到其他客户端*/public void sendInfoToOtherClients(String msg, SocketChannel socketChannel) {try {System.out.println("消息转发中.....");System.out.println("sendInfoToOtherClients thread name "+ Thread.currentThread().getName());for (SelectionKey selectionKey : selector.keys()) {Channel targetChannel = selectionKey.channel();if (targetChannel instanceof SocketChannel && targetChannel != socketChannel) {SocketChannel targetSocketChannel = (SocketChannel) targetChannel;targetSocketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes()));}}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static void main(String[] args) {GroupChatService groupChatService = new GroupChatService();groupChatService.listen();}
}
-
案例说明:
- Select是NIO中标准网络编程API,可以实现应用陈旭通过一个阻塞对象监听多路连接请求
- Reactor对象通过Select监控客户端请求事件,收到事件后通过dispatch进行分发
- 如果是建立连接请求的事件,那么直接有Acceptor通过Accept处理连接请求,然后传家一个Handler对象用这个新创建的Handler来完成连接之后的业务
- 如果不是建立连接事件,那么Reactor会分发调用连接对应的Handler来响应
- Handler会完成Read ---- 业务处理 ---- Send的完整业务流程
-
优缺点分析
- 优点:模型简单,没有多线程,进程通讯,没有线程竞争问题,全部在一个线程中完成,编程难度低
- 缺点:明显的性能问题,只有一个线程,无法完全发挥多核CPU的性能。Handler在处理某个连接上的业务时候,整个进程无法处理其他连接事件,很容易导致性能瓶颈。
- 缺点:可靠性问题,线程意外终止,或者线程进入死循环,会导致整个系统通讯模块不可用,不能接受和处理外部消息,造成节点故障
- 使用场景:客户端数量少,业务处理非常快,比如Redis的业务处理事件复杂度O(1)
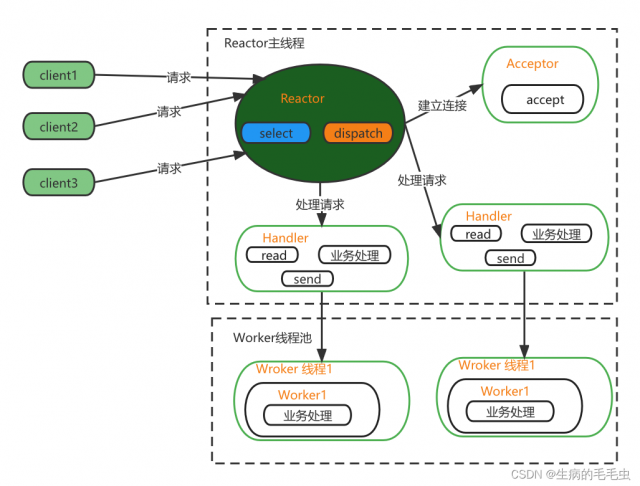
单Reactor 多线程模型
-
单Reactor多线程图示说明
- Reactor对象通过Select监控客户端请求事件,收到事件后,通过Dispatch进行分发
- 如果建立连接请求后,如果是Acceptor连接事件那么我们通过accept处理这个请求,然后创建一个Handler对象处理完成连接后的各种事件
- 如果不是连接请求,那么由Reactor分发调用连接对应的handler来处理
- handler之负责响应事件,不做具体的业务处理,通过read读取数据后,会分发给后面的worker线程池的某个线程处理业务
- worker线程池会分配独立的线程完成真正的业务,并且将结果返回给handler
- handler收到响应后,通过send将结果返回给client
-
方案优缺点
- 优点:可以充分利用CPU多核处理能力
- 缺点:多线程数据共享范问比较复杂,Reactor处理所有的事件的监听和响应,在单线程运行,在高并发场景容易出现性能瓶颈
主从Reactor多线程模型
- 针对单Reactor多线程模型中,Reactor在单线程中运行,高并发下这部分容易成为性能瓶颈,可以让Reactor在多线程中运行。

- 上图方案说明:
- Reactor主线程MainReactor对象通过select监听连接事件,收到事件后,通过Acceptor处理连接事件
- 当Acceptor处理完连接事件后,MainReactor将连接分配给SubReactor
- subReactor将连接加入到连接队列进行监听,并且川江handler进行各种事件处理
- 当有新的事件发生时候,subReactor就会调用对应的handler处理
- handler通过read读取数据,分发给后面的worker线程处理
- worker线程池分配度的worker线程进行业务处理,并且返回结果
- handler收到响应的结果后,在通过,send将结果返回给client
- Reactor主线程可以对应多个Reactor子线程,即MainReactor可以关联多个SunReactor
Scalable IO in Java对Multiple Reactors原理图解

-
Scalable IO in Java 原文链接
-
方案优缺点说明:
- 优点:父线程于子线程的数据交互简单职责明确,父线程只需要接收新链接,子线程完成后续的业务处理
- 优点:父线程与子线程的数据交互简单,Reactor主线程只需要把新链接传给子线程,子线程无需返回数据
- 缺点:编程复杂度高
- 结合实例:这种模型在许多项目中广泛使用,包括Nginx主从Reactor多进程模型,Memcached主从多线程,Netty主从多线程模型的支持。
Reactor模式总结
- 单Reactor单线程,酒店的门童,服务员是同一个人,全程为客户服务
- 单Reactor多线程,1个门童,多个服务员,门童之负责接待,转给服务员
- 主从Reactor多线程,多个门童,多个服务员
Reactor模式优点
-
响应快,不必为单个同步事件所阻塞,虽然Reactor本身是同步的
-
可以最大程度避免复杂多线程同步问题,并且避免了多线程/进程的切换开销
-
扩展性好,可以方便的通过增加Reactor实例个数来充分利用CPU资源
-
复用新好,Reactor模型本身与具体事件处理逻辑无关,具有很高的复用性。
-
下一篇:Netty启动流程源码剖析
本文链接:https://my.lmcjl.com/post/16024.html
展开阅读全文

4 评论