目录
一.线程创建
Lambda创建一个线程
基础格式
举例
运行结果
二.线程中断
第一种:设置变量方法
举例
运行结果
第二种:interrupted()方法
举例
运行结果
三.线程等待
举例
运行结果
四.线程休眠
举例
五.获取线程实例
举例
运行结果
一.线程创建
线程的创建一般来说有五种
1.lambda
2.继承Thread,重写run
3.实现Runnable,重写run
4.使用匿名内部类,继承Thread,重写run
5.使用匿名内部类,实现Runnable,重写run
这我的这篇博客详细介绍了这五种方法的代码和实现
Java创建多线程的五种写法_幻荼的博客-CSDN博客
在这里我就只写lambda的那种,因为这个最方便最推荐
Lambda创建一个线程
基础格式
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
//此处写线程实现的代码}});thread.start();
//此处写主函数的代码}
}举例
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread thread = new Thread(()->{int i = 0;while(i<5){System.out.println("阿米娅"+i);i++;}});thread.start();int j = 10;while(j>5){System.out.println("爱莉希雅"+j);j--;}}
}运行结果
(线程和主程序运行结果可能会调换顺序)

二.线程中断
一般来说有两种方法
1.自己设置变量进行判断
2.使用interrupted()方法进行判断
第一种:设置变量方法
就是自己设置一个变量,如果满足则线程继续执行,如果不满足则结束
举例
public class demo8 {
//此处设置了一个名字叫做isQuit的boolean的变量作为线程是否继续的条件public static boolean isQuit = true;public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{int i = 0;
//如果这个变量一直为true,那么这个线程会一直执行下去,每隔一秒打印一次while(isQuit){System.out.println(i);i++;try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});t1.start();
//在线程执行5秒后,将变量变为false,那么线程就会停止执行Thread.sleep(5000);isQuit=false;}
}
运行结果
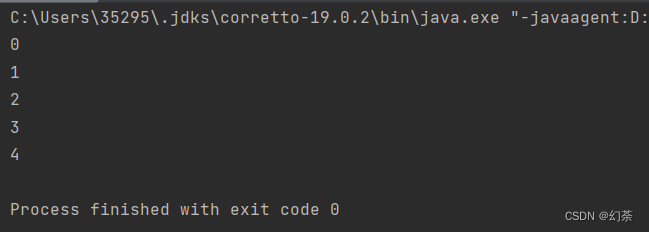
上面这种方式比较温柔不会弹出错误
而下面这种使用函数的方式会提醒更加醒目
第二种:interrupted()方法
相当于使用函数来代替我们的判断方法
举例
public class demo9 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {int i = 0;Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{int j = i;
//此处的Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()就相当于判断是否被打断
//如果没有被interrupt打断,那么结果一直是false,直到调用interrupt方法后变为truewhile(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){System.out.println(j);j++;try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});t1.start();Thread.sleep(5000);
//调用interrupt方法,打断t1.interrupt();}
}
关于Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()这个函数大家可以这么理解

运行结果
这个时候就会报错了
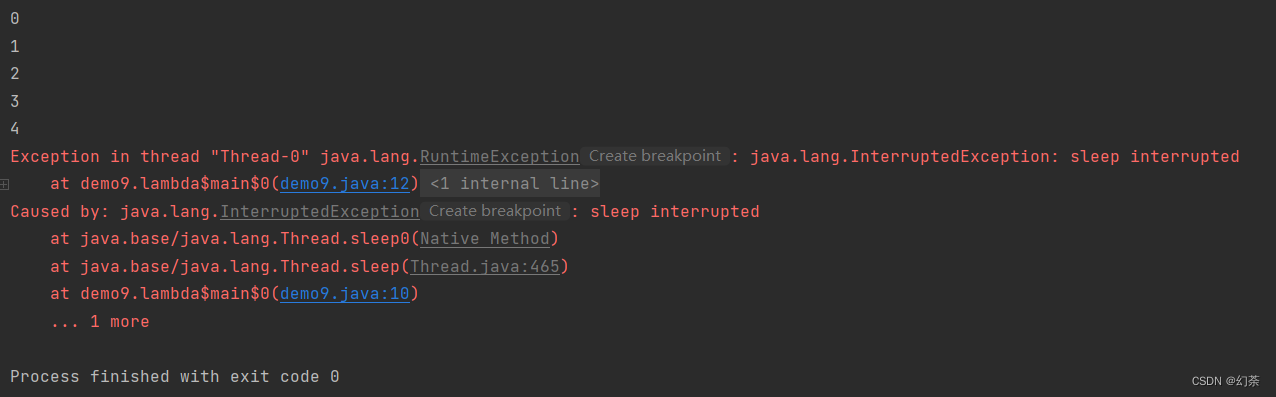
三.线程等待
简单来说就是让某个线程先运行
等该线程运行完毕后再运行下面的代码
举例
public class demo10 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread(()-> {System.out.println("我是线程1,我有join我先执行");});Thread t2 = new Thread(()-> {System.out.println("我是线程2,我也有join但是我后面join,我后你一步执行");});t1.start();t2.start();t1.join();t2.join();System.out.println("我是函数,我没有join只有等你们都运行完毕我在运行");}
}
运行结果
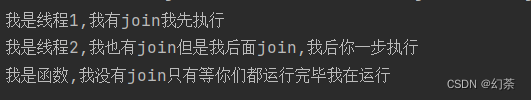
只要调用了join,那么后面的代码就一定后执行
四.线程休眠
就是让该线程休眠多少ms
(1s=1000ms)
举例
public class demo11 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{try {Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println("我先睡五秒再打印");});t1.start();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println(i);Thread.sleep(1000);}}
}
运行结果

由于程序是并发运行的,但是运行线程的时候遇到了sleep,短暂休眠了5秒
这个时候就先打印了函数,五秒之后再打印线程里面的内容,这就是休眠sleep的用法!
五.获取线程实例
不就是我们在打断方法的时候用过的Thread.currentThread()吗
举例
public class demo12 {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t1 = Thread.currentThread();System.out.println(t1.getName());}
}
运行结果

本文链接:https://my.lmcjl.com/post/3049.html

4 评论